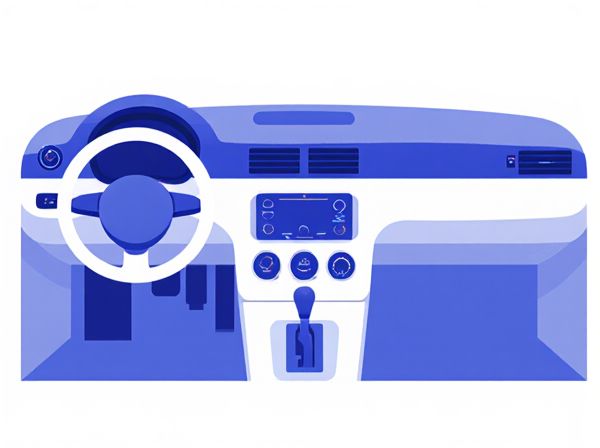
Photo illustration: Flat Dashboard Layout vs Driver-Oriented Dashboard
A flat dashboard layout offers a clean, minimalist design that prioritizes simplicity and easy access to information without clutter. In contrast, a driver-oriented dashboard enhances ergonomics by angling controls and displays toward the driver, promoting safety and intuitive interaction. Your choice depends on whether you value streamlined aesthetics or optimized functionality tailored for the driver's experience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flat Dashboard Layout | Driver-Oriented Dashboard |
|---|---|---|
| Design Focus | Uniform layout centered on passengers | Angled controls and displays toward the driver |
| Usability | Equal accessibility for all occupants | Enhanced driver control and quick access |
| Safety | Standard visibility, may require more driver focus | Minimized distraction with driver-centric info |
| Ergonomics | Neutral physical interaction | Optimized for driver comfort and reach |
| Technology Integration | Balanced tech layout for all passengers | Priority on driver interfaces like HUDs and controls |
| Typical Use Case | Family cars, shared driving | Sports cars, performance-oriented vehicles |
Introduction to Dashboard Layouts
Dashboard layouts play a crucial role in enhancing driver experience and safety. The Flat Dashboard Layout offers a streamlined, minimalist interface that prioritizes ease of access and reduces cognitive load. In contrast, the Driver-Oriented Dashboard is ergonomically designed to position essential controls and displays within the driver's immediate reach and sightline, improving reaction time and usability.
Defining Flat Dashboard Layouts
Flat dashboard layouts present information on a single, unified screen without layering or nested menus, enhancing quick data scanning and comprehensive visibility. This design emphasizes simplicity and minimalism, using uniform panels and consistent visual hierarchy to avoid cognitive overload. Flat layouts prioritize accessibility and direct interaction, making them ideal for users who require simultaneous monitoring of various performance metrics.
What is a Driver-Oriented Dashboard?
A Driver-Oriented Dashboard is designed to prioritize the driver's line of sight and ease of interaction, placing critical controls and information within immediate reach to enhance safety and usability. It features angled instrument panels and centralized displays that reduce distraction by minimizing the need for head movement. This layout contrasts with a traditional flat dashboard by optimizing ergonomics and functionality tailored specifically for driver convenience and real-time vehicle status monitoring.
Visual Differences at a Glance
The Flat Dashboard Layout features a clean, minimalist design with evenly spaced information panels and uniform typography, emphasizing simplicity and ease of scanning. In contrast, the Driver-Oriented Dashboard is angled and contoured towards the driver, with clustered controls and displays focused on ergonomics and quick access. Visual cues such as larger, prioritized gauges and tactile buttons differentiate the Driver-Oriented Dashboard from the more static, grid-based Flat Layout.
Ergonomics and User Experience
Flat dashboard layouts offer a minimalist design that enhances visual clarity and reduces cognitive load, improving overall user experience by allowing quick access to essential information. Driver-oriented dashboards prioritize ergonomics by angling controls and displays toward the driver, minimizing distraction and promoting safer interaction during driving. Both approaches impact user experience distinctly: flat layouts support simplicity and aesthetics, while driver-oriented designs focus on intuitive control placement and operational efficiency.
Impact on Driver Safety
A Driver-Oriented Dashboard enhances driver safety by providing intuitive access to critical controls and information, reducing distraction and enabling quicker response times. Flat Dashboard Layouts can cause drivers to search for essential data, increasing cognitive load and reaction time, which may compromise safety. Prioritizing ergonomics and user-centric design in driver-oriented dashboards significantly lowers the risk of accidents.
Customization and Personalization Options
Flat dashboard layouts offer straightforward customization with modular widgets allowing users to rearrange and resize components freely according to their workflow preferences. Driver-oriented dashboards provide a higher level of personalization by dynamically adapting interface elements to individual driving habits, real-time conditions, and safety priorities using AI-driven data inputs. Both layouts aim to enhance user interaction, yet flat designs prioritize user-initiated control while driver-oriented dashboards optimize situational responsiveness and personalized assistance.
Technology Integration and Displays
Flat dashboard layouts emphasize seamless technology integration with centralized touchscreen displays, providing intuitive access to infotainment and vehicle settings. Driver-oriented dashboards prioritize ergonomic design by angling digital instrument clusters and controls towards the driver to enhance focus and minimize distraction. Advanced display technologies like OLED and HUDs are increasingly employed in both layouts to deliver high-resolution graphics and real-time data, improving visibility and overall user experience.
Pros and Cons of Each Layout
Flat dashboard layouts offer a clean, organized interface with easy visibility of multiple data points, enhancing overall situational awareness, but they may overwhelm drivers with information overload and reduce focus during critical driving tasks. Driver-oriented dashboards prioritize ergonomics and accessibility by angling controls and displays towards the driver, improving usability and safety, though this design can limit the visibility of information for passengers and potentially reduce aesthetic appeal. Selecting between these layouts depends on balancing comprehensive data access against ergonomic efficiency and safety considerations.
Choosing the Right Dashboard for Your Needs
Choosing the right dashboard depends on user roles and task complexity; a flat dashboard layout provides a broad overview with equal access to multiple data points, ideal for monitoring and quick assessments. In contrast, a driver-oriented dashboard is tailored for specific drivers, presenting critical information prominently to enhance decision-making efficiency in real-time operations. Understanding the primary use case and user priorities ensures the dashboard delivers relevant insights and improves overall workflow effectiveness.
 caratoz.com
caratoz.com