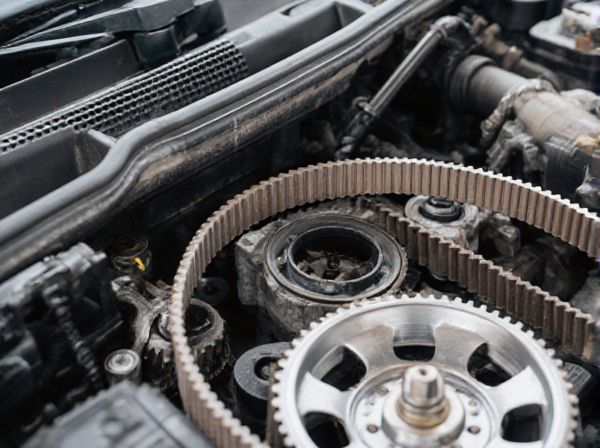
Photo illustration: Direct-Driven Camshaft vs Remote-Driven Camshaft
Direct-driven camshafts offer precise timing and reduced mechanical complexity by connecting the camshaft directly to the crankshaft, enhancing engine responsiveness. Remote-driven camshafts use belts or chains, allowing for flexible placement and easier maintenance but may introduce slight timing delays. Choosing the right system depends on your engine design priorities, such as performance accuracy or service convenience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Direct-Driven Camshaft | Remote-Driven Camshaft |
|---|---|---|
| Timing Belt Connection | Direct connection from crankshaft to camshaft | Timing belt drives a shaft that in turn drives camshaft |
| Component Complexity | Simple, fewer parts | More complex, additional intermediate shaft |
| Maintenance | Easier alignment and replacement | More involved due to extra components |
| Durability | Lower risk of timing belt slack | Potential for increased wear on intermediate parts |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing and repair cost | Higher due to added components |
| Application | Common in compact, efficient engines | Used in engines requiring camshaft placement flexibility |
Introduction to Camshaft Drive Systems
Direct-driven camshafts connect directly to the crankshaft, providing precise timing and improved engine efficiency by eliminating intermediary components. Remote-driven camshafts use belts, chains, or gears to transmit motion from the crankshaft, allowing greater flexibility in engine layout but potentially introducing timing delays and wear. Understanding the differences in these camshaft drive systems is crucial for optimizing engine performance and durability.
What is a Direct-Driven Camshaft?
A direct-driven camshaft is a camshaft configuration where the camshaft is connected directly to the crankshaft, typically using gears or a timing chain, ensuring precise timing and minimal power loss. This setup improves engine efficiency by providing accurate valve timing and reducing the complexity and maintenance associated with additional transmission components. Direct-driven camshafts are commonly found in high-performance and modern engines for enhanced durability and responsiveness.
What is a Remote-Driven Camshaft?
A remote-driven camshaft is a camshaft that is positioned away from the crankshaft and connected via a chain, belt, or gear mechanism, allowing for more flexible engine design and packaging. Unlike direct-driven camshafts that are mounted directly on the crankshaft, remote-driven camshafts enable optimized valve timing and reduced mechanical stress by utilizing indirect drive systems. This configuration is common in modern engines to achieve better performance, noise reduction, and maintenance accessibility.
Key Design Differences
Direct-driven camshafts are mechanically connected to the crankshaft via gears or chains, enabling precise valve timing with minimal power loss. Remote-driven camshafts utilize belts or chains routed through idlers or tensioners, offering greater flexibility in engine layout but introducing potential timing variability. Key design differences hinge on complexity, spatial arrangement, and durability under varying operating conditions.
Performance Comparison
Direct-driven camshafts provide more precise valve timing and quicker throttle response due to their direct mechanical connection to the crankshaft, enhancing overall engine performance. Remote-driven camshafts, often operated via timing belts or chains, can introduce slight delays and less accurate timing but offer easier maintenance and greater design flexibility. Performance-wise, direct-driven camshafts excel in high-revving engines where precise timing is critical, while remote-driven systems are preferred in applications prioritizing durability and cost-effectiveness.
Reliability and Maintenance
Direct-driven camshafts offer enhanced reliability by minimizing mechanical linkages, reducing wear points and potential failure compared to remote-driven camshafts. Maintenance is simplified for direct-driven systems due to fewer moving parts and easier access, resulting in lower downtime and reduced service costs. Remote-driven camshafts, while sometimes necessary in complex engine layouts, often require more frequent inspection and alignment checks to maintain optimal performance.
Application and Use Cases
Direct-driven camshafts are commonly used in high-performance engines and motorcycles where precise valve timing and compact design are critical, offering reduced mechanical complexity and improved responsiveness. Remote-driven camshafts find applications in heavy-duty industrial engines and larger automotive engines, allowing flexibility in engine design by positioning the camshaft away from the crankshaft for easier maintenance and cooling. Both systems serve specific needs based on engine size, performance demands, and spatial constraints in automotive and industrial machinery.
Cost and Complexity Considerations
Direct-driven camshafts typically incur higher initial costs due to intricate manufacturing and precise alignment requirements but offer reduced maintenance expenses over time. Remote-driven camshafts present lower upfront costs and simpler installation with fewer precision components, although they may experience increased complexity in timing adjustments and potential long-term wear issues. Evaluating cost-effectiveness involves balancing the direct-driven system's durability against the remote-driven option's economic and installation simplicity advantages.
Pros and Cons of Each System
Direct-driven camshafts offer precise timing and reduced power loss since the camshaft is directly connected to the crankshaft, enhancing engine efficiency and responsiveness. However, they contribute to increased engine friction and mechanical complexity, potentially leading to higher maintenance costs and limited flexibility in cam timing adjustments. Remote-driven camshafts provide greater design flexibility and easier integration of variable valve timing systems, reducing mechanical stress and wear, though they may introduce slight delays in valve response and increased power transmission losses.
Choosing the Right Camshaft Drive for Your Engine
Choosing the right camshaft drive for your engine depends on factors such as performance goals, engine layout, and maintenance preferences. Direct-driven camshafts offer precise timing and reduced complexity, ideal for high-performance applications requiring accuracy and durability. Remote-driven camshafts provide flexibility in engine design and easier access for adjustments, making them suitable for custom setups and engines with space constraints.
 caratoz.com
caratoz.com